Tx flow control mikrotik что это
Flow Control — что это? (включать или нет)

Включать или нет: только если наблюдаются странности в работе сети при большом количестве входящего трафика (обычно для игр включать ненужно).
Эта настройка предназначена для ситуаций, когда входящего трафика так много, что может произойти ошибка переполнения буфера, при котором оборудование отправляет команду паузы, после которой повторил отправку данных спустя некоторое время. Если подобную команду не послать — будет перегрузка, часть данных может потеряться, в итоге могут быть например глюки в игре. Также стоит понимать, что из-за команды паузы — увеличится значение пинга.
Функция полезна, когда происходит загрузка большого количества данных, например торренты. Игры обычно не имеют настолько активный трафик.
Функция например присутствует в сетевом адаптере D-Link DFE-550TX.
Flow Control включать стоит, когда наблюдаются непонятные задержки, обрывы, пропадания, лаги, тормоза при просмотре онлайн-видео. Также эту опцию включают при соединении разноскоростного оборудования или разноскоростных сетей, образно говоря, чтобы скоростная сеть не забила трафиком порт менеескоростной.
Опция сетевого адаптера Realtek:
Однако также спокойно может встречаться и в адаптерах других производителей, например Intel, Atheros.
Кстати открыть диспетчер устройств можно простым способом — зажмите Win + R, появится окошко Выполнить, вставьте команду devmgmt.msc и нажмите ОК.
Надеюсь данная информация оказалась полезной.
Ethernet
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet
Standards: IEEE 802.3
Properties
Read-only properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| running (yes | no) | Whether interface is running. Note that some interface does not have running check and they are always reported as «running» |
| slave (yes | no) | Whether interface is configured as a slave of another interface (for example Bonding) |
| switch (integer) | ID to which switch chip interface belongs to. |
Menu specific commands
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| blink ([id, name]) | Blink Ethernet leds |
| monitor ([id, name]) | Monitor ethernet status. Read more>> |
| reset-counters ([id, name]) | Reset stats counters. Read more>> |
| reset-mac-address ([id, name]) | Reset MAC address to manufacturers default. |
| cable-test (string) | Shows detected problems with cable pairs. Read More >> |
Monitor
To print out a current link rate, duplex mode, and other Ethernet related properties or to see detailed diagnostics information for transceivers, use /interface ethernet monitor command. The provided information can differ for different interface types (e.g. Ethernet over twisted pair or SFP interface) or for different transceivers (e.g. SFP and QSFP).
Properties
Example output of an Ethernet status:
Example output of a SFP status:
Detect Cable Problems
Cable test can detect problems or measure the approximate cable length if the cable is unplugged on the other end and there is therefore, «no-link». RouterOS will show:
Here is example output:
In the above example, the cable is not shorted but “open” at 4 meters distance, all cable pairs equally faulty at the same distance from the switch chip.
Currently cable-test is implemented on the following devices:
Note: Currently cable-test is not supported on Combo ports.
Stats
Using /interface ethernet print stats command, it is possible to see a wide range of Ethernet related statistics. The list of statistics can differ between RouterBoard devices due to different Ethernet drivers. The list below contains all available counters across all RouterBoard devices. Most of the Ethernet statistics can be remotely monitored using SNMP and MIKROTIK-MIB.
For example, output of Ethernet stats on hAP ac2 device:
Tx flow control mikrotik что это
Thu Dec 10, 2015 1:47 am
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Thu Dec 10, 2015 11:51 pm
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 12:08 am
FCS and Flow Control should not be be related. FCS (Frame Check Sequence) tells you that you are getting CRC errors on the link. Flow control should only be needed if you are running at near 100% link capacity.
That said, FCS errors are common caused by misbehaving hardware. often it could be as simple as a half-duplex link, or outdated firmware in a networked device. In more extreme situations you can look into the hardware itself. Even a cheap or damaged cat5 cable can cause framing errors. Hell, I’ve had them because a cable was run too close to light fixture.
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 1:55 am
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 2:14 am
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 2:23 am
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 10:43 pm
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Fri Dec 11, 2015 10:45 pm
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Sat May 07, 2016 2:07 am
So nobody can really switch it on? I’d presume every traffic nowadays has VoIP packages in it as well (if you are a internet provider)?
We have tcp throughput issues and are looking for solutions. We thought to have it found since all our network (full MT, hundreds of units) have it ‘off’ by default.
For a moment we thought this might be the solution, but we DO have clients using VoIP. so where are we now?
Show your appreciation of this post by giving me Karma! Thanks.
WISP operator based on MT routerboard & ROS.
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Sat May 07, 2016 7:58 am
What you will need to do is analyze your traffic, figure out where it’s all being used and then figure out if you have to buy more bandwidth, or if you need to do some QoS.
Re: Flow Control, should I use it?
Sat May 07, 2016 12:39 pm
What you will need to do is analyze your traffic, figure out where it’s all being used and then figure out if you have to buy more bandwidth, or if you need to do some QoS.
Bandwidth can’t be the problem. We have a 300/300Mb symmetric line and rarely see combined client traffic coming close to 200.
On my PC’s we do at times tests and by opening several download streams, preferably on 2 or 3 PC’s we get up to max. 295Mbps download traffic.
Upload with www.speedtest.net usually shows close to 300Mbps..
If there are bottlenecks, it’s in the network. But like any other provider we have to oversubscribe, even at the level of an P2MP network. I don’t know if there are any operators that keep the possible max clients usages within levels the AP can handle (100Mb connected AP could only server 10 x 10Mb contracted clients? Bad, and thus very rare business model.)
Every operator sells more bandwidth than he could ever deliver if all his clients would demand their contracted speed at the same time. That counts for all network infrastructures. If it is internet, the electricity company’s, the national road infrastructure or the domestic water company.
I know the national adsl provider has some 10 million clients and they are all sold 10Mbps. How much would that be if all would use that at the same time? Not a single network can deal with that. So we all work with oversubscribing our network at some levels. We all have to make educated best guesses at which points the first priority lies to upgrade which bottleneck to produce better overall capacity again and again.
So bottleneck’s are part of every network. And thus mixed capacity links are part of a network.
We have as said 300/300Mb capacity coming to us via a Cisco router that connects by gigabit to our CCR. From here we have gigabit Ethernet going to several back-haul radio’s. Some of these maintain a 80Hz ac link and some only a 20Mhz ‘n’ link.
Than on the other side we see some radio’s connected with 100M to the next radio (AP or just a new link) where others have yet again gigabit connections to the next routers.
In general I would say that each client requested packages that comes in from the 300Mb symettric would ‘see’ some gigabit links, some 100M links, some highspeed ‘ac’ radio backhaul, some medium speed 20Mhz ‘n’ backhaul towards an AP that usually connects to ‘n’ (some still single chain) clients where these CPE’s than connect with 100M to client’s devices.
Since download is the bulk of traffic I should start looking from where the traffic come in?
1st capacity is 300Mb (‘pipe’ from provider to Cisco with 300Mb)
2nd: 1000M cable to CCR. Presume here no traffic flow control needed?
3rd: New 1000M cable to ‘ac’ radio with 80Mhz channel (we could ‘pump’ some 250-300Mb tcp over it. It’s actually 2 links with OSPF simulated duplex)
4th: That radio link capable of 250-300Mbps
5th: Other radio wich connects with 1000M to another CCR.
6th: This CCR routes traffic to 4 new bachauls, all of the radio’s connect with 1000M to this CCR.
6tha: This CCR also through a switch supplies 3 x AP that serves some 75 clients. All connections are Gig but radio links are much weaker. Conn. rate in generall 80Mb.
7th: New backhauls to new remote locations. Some have 40Mhz ‘n’ links set to 270Mbps conn. rate, other have 130Mbps conn. rate 20Mhz channel.
8th etc. More links, more AP’s
Some clients in our network are only reached after the package travels over 5 wireless links (including the AP to CPE link) and had seen at least 15 Mikrotik routers in our network before it has reached clients Wifi router or PC.
A small minority of clients would use VoIP.
70 of our clients now connect with PPPoE and within a month this should be 100%
The PPPoE server in our gateway creates single queues for each user depending to its assigned contract. Highest speeds is 50Mb download, bulk is 20Mb and 40% only 10Mb.
What would be your best strategy if we talk about flow control?
Show your appreciation of this post by giving me Karma! Thanks.
WISP operator based on MT routerboard & ROS.
Manual:Interface/Ethernet
Applies to RouterOS: v3, v4+
Contents
Summary
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet
Standards: IEEE 802.3
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| running (yes | no) | Whether interface is running. Note that some interface does not have running check and they are always reported as «running» |
| slave (yes | no) | Whether interface is configured as a slave of another interface (for example Bonding) |
| switch (integer) | ID to which switch chip interface belongs to. |
Menu specific commands
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| blink ([id, name]) | Blink Ethernet leds |
| monitor ([id, name]) | Monitor ethernet status. Read more>> |
| reset-counters ([id, name]) | Reset stats counters. Read more>> |
| reset-mac-address ([id, name]) | Reset MAC address to manufacturers default. |
| cable-test (string) | Shows detected problems with cable pairs. Read More >> |
Monitor
To print out a current link rate, duplex mode, and other Ethernet related properties or to see detailed diagnostics information for transceivers, use /interface ethernet monitor command. The provided information can differ for different interface types (e.g. Ethernet over twisted pair or SFP interface) or for different transceivers (e.g. SFP and QSFP).
Example output of an Ethernet status:
Example output of a SFP status:
Detect Cable Problems
Cable test can detect problems or measure the approximate cable length if the cable is unplugged on the other end and there is therefore, «no-link». RouterOS will show:
Here is example output:
In the above example, the cable is not shorted but “open” at 4 meters distance, all cable pairs equally faulty at the same distance from the switch chip.
Currently cable-test is implemented on the following devices:
Note: Currently cable-test is not supported on Combo ports.
Stats
Using /interface ethernet print stats command, it is possible to see a wide range of Ethernet related statistics. The list of statistics can differ between RouterBoard devices due to different Ethernet drivers. The list below contains all available counters across all RouterBoard devices. Most of the Ethernet statistics can be remotely monitored using SNMP and MIKROTIK-MIB.
For example, output of Ethernet stats on hAP ac2 device:
Switch
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet switch
This submenu allows configuration of certain RouterBoard switch chip features. Read more >>.
PoE out
Sub-menu: /interface ethernet poe
PoE out settings are only available on RouterBOARD devices that have this hardware feature present. See more here: PoE-Out
ИТ База знаний
Полезно
— Онлайн генератор устойчивых паролей
— Онлайн калькулятор подсетей
— Руководство администратора FreePBX на русском языке
— Руководство администратора Cisco UCM/CME на русском языке
— Руководство администратора по Linux/Unix
Навигация
Серверные решения
Телефония
FreePBX и Asterisk
Настройка программных телефонов
Корпоративные сети
Протоколы и стандарты
Все про трафик с Netflow на MikroTik
Разбор полетов пакетов
Полный курс по Сетевым Технологиям
В курсе тебя ждет концентрат ТОП 15 навыков, которые обязан знать ведущий инженер или senior Network Operation Engineer
Помимо мониторинга и анализа трафика, с помощью Traffic Flow, администратор может выявлять различные проблемы, которые могут появляться в сети, а также анализировать и оптимизировать общие сетевые характеристики.
Поскольку Traffic Flow полностью совместим с Cisco Netflow, то он может использоваться различными утилитами, которые разработаны для Netflow.
Traffic Flow поддерживает следующие версии Netflow:
Настройка
Итак, для того, чтобы начать собирать статистическую информацию о трафике, необходимо сначала включить Traffic Flow и определиться с каких интерфейсов осуществлять сбор. Делается это при помощи комбинации следующих команд:
После того как мы включили Traffic Flow и определились с интерфейсами, с которых хотим получать информацию о потоках, необходимо настроить хост назначения, который будет получать данную информацию (в терминологии Netflow такой хост называется коллектором). Делается это при помощи следующей команды
Пример
Рассмотрим пример конфигурации Traffic Flow на роутере Mikrotik
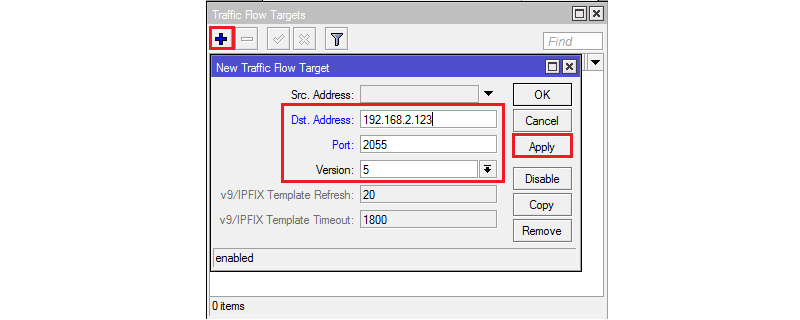
Допустим мы хотим собирать статическую информацию о трафике, который проходит через интерфейс ether3 нашего роутера и отправлять её на коллектор по адресу 192.168.2.123 используя 5 версию протокола. В этом случае конфигурация может выглядеть следующим образом:
Сначала включаем Traffic Flow и указываем интерфейс
Затем указываем адрес коллектора, стандартный порт и версию протокола 5:
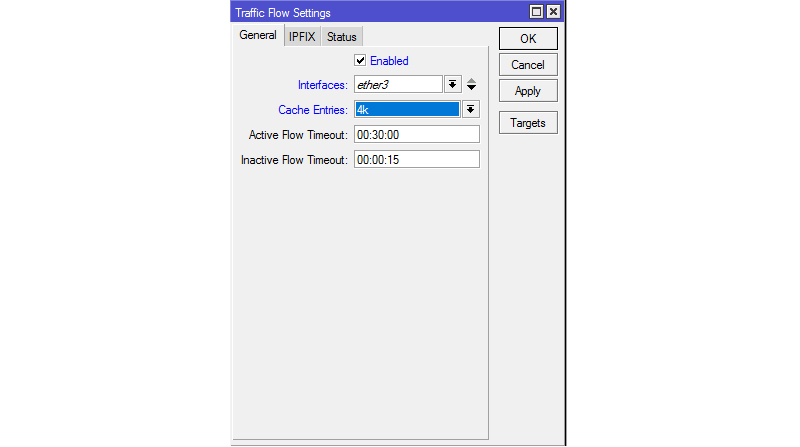
Если Вы предпочитаете консоли утилиту WinBox, то для настройки Traffic Flow левом меню откройте пункт IP и выберите Traffic Flow, перед Вами откроется следующее окно:
Необходимо включить Traffic Flow, поставив галочку напротив Enabled и выбрать желаемый интерфейс для сбора информации.
После этого переходим на вкладку Targets и добавляем параметры коллектора, достаточно внести IP адрес, порт и версию. После этого нажимаем на кнопку Apply
После этого наш роутер начнет отправлять информацию на коллектор. Если вы хотите указать несколько коллекторов, то это можно сделать, используя разные версии протокола и номера UDP портов.
Полный курс по Сетевым Технологиям
В курсе тебя ждет концентрат ТОП 15 навыков, которые обязан знать ведущий инженер или senior Network Operation Engineer